Only the most myopic could have failed to notice that times are changing in terms of engine technology. In the on-highway automotive sector as well as for the off-highway construction machine segment, manufacturers are looking to lower tailpipe emissions. Similar technologies have been employed in both on-highway and off-highway sectors, although those solutions have been adapted to better suit the specific needs of those very different operating environments.
For heavy road vehicles such as buses and trucks or construction machines, tailpipe emissions from the latest generation diesels are a mere fraction of what they were just 10-15 years ago. Successive waves of regulations in Europe and the US have encouraged firms to develop far cleaner diesel power systems that produce far lower quantities of nitrous oxide or particulates than earlier designs.
For off-highway machines, the development of engines meeting the strict Tier 4 Final and Stage IV emissions requirements for the US and European market respectively have seen diesel suppliers using sophisticated fuel injection, in-cylinder and aftertreatment technologies. Innovative, single module aftertreatment systems have been developed that are 60% smaller and 40% lighter than earlier generation technologies. And firms are currently working on engines to meet the coming Stage V emissions targets that will apply to equipment in Europe.
The use of these diesel engines depends on the availability of clean fuel types with very low sulphur levels. Developing countries have not previously had access to such clean fuels, but this is changing and China has already implemented emissions requirements equivalent to the Tier 3/Stage IIIA levels in the US and Europe, with the prospect of meeting the tougher requirements in the future. India too has pledged to adopt the Tier 4 Final/Stage IV levels in the future.
Looking further ahead however, engine firms are now working towards future alternatives with lower emissions still. Not only are nitrous oxides and particulates being targeted for reduction, firms are also working on powertrains with lower CO2 emissions.
Hybrid powertrains have moved from being interesting concepts to real world solutions. The automotive sector has seen a strong take-up in hybrid vehicles over the past 10 years and Toyota’s Prius model in particular has been a massive sales success. Once a rare sight on the road, hybrid vehicles have become common in the passenger car market, as well as for buses. Excavators for construction machines too are now being offered in hybrid versions, with
Equipment manufacturers are keen to offer alternative power solutions, as Alexander Greschner, a member of the executive board of
Research is being carried out into alternative fuel types with lower levels of nitrous oxides and particulates, with many of the leading companies developing solutions. Both
Cummins recently stated that the company is now positioned to lead in current and future technologies, including its core business, electric drives, alternative fuels and power solutions, as well as in digital capabilities, data and analytics. Tom Linebarger, Cummins Chairman and CEO said, “We are prepared to provide a range of power technologies to our customers from diesel and natural gas to fully electric and hybrid powertrains to ensure they always have the best solution for their application.”
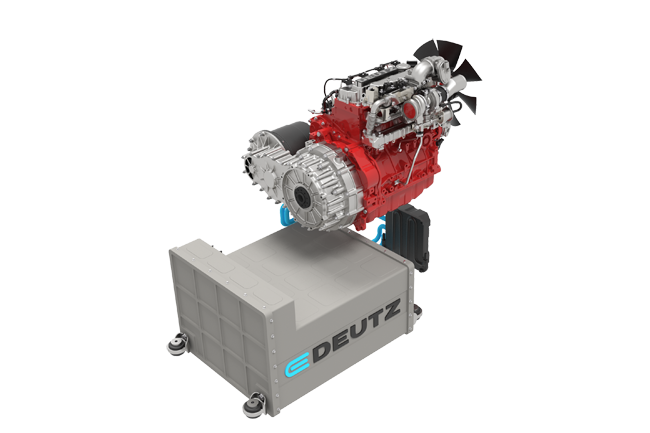
“Going forward, we will be positioning ourselves much more strongly as a supplier of innovative drive systems and focusing on alternative fuels,” said chairman of the Deutz board of management Dr Frank Hiller. “The new E-Deutz strategy, for example, includes hybrid solutions, partial electrification and electric drive components. And the proceeds from the sale of property are allowing us to invest even more heavily in technology, innovation and service.”
Cummins offers natural gas engine systems that suit use in urban areas as they can help address air quality issues. Natural gas engine technology can have a very low carbon footprint and vehicles have a much longer range, maintenance is improved, and fueling station availability has expanded.
The company is working on commercialising its electric drive capabilities and is is exploring partnering with others on developing technology for energy storage, power electronics, traction motor systems and component control. The company says it will be offering battery electric and plug-in hybrids in 2019 for commercial and industrial markets.
Additionally, Cummins has invested in research and development projects to build capability to develop products using a wide range of fuels. The firm is developing high efficiency petrol technology that can deliver diesel-like performance and durability, meeting the most stringent emissions requirements while maintaining competitive fuel economy.
Longer term, the company says that its research and technology continues to investigate the viability of alternatives like bio-fuels, synthetic fuels and hydrogen. Cummins has also invested in exploratory projects for proton exchange membrane and solid oxide fuel cell technologies, both with increasing potential to offer superior power density over the traditional internal combustion engine.
Meanwhile in a joint research project with the University of Rostock and the Thünen Institute, Deutz has developed a natural gas engine for tractors. The project involved Deutz engineers converting a diesel engine to run on natural gas and then installing it in a tractor. The aim was to reduce pollutants and CO2 emissions without any loss of performance. The advantage of natural gas is that it burns much more cleanly than petrol or diesel. It produces less CO2, and emissions of nitrogen oxides and particulates are also substantially lower. While the last two can be contained relatively easily with modern exhaust aftertreatment, CO2 emissions are primarily dependent on the type and quantity of fuel used.
Converting the engine to run on natural gas required several major component adaptations. The self-igniting diesel injectors first had to be replaced with a spark ignition system, and the pistons and cylinder head had to undergo mechanical adjustments. Deutz says that a key factor was analysing and understanding the combustion process.
But these two engine firms are not the only companies in the off-highway sector that have announced the development of alternative powertrain projects. Transmission specialist Oerlikon Graziano unveiled its range of hybrid transmission systems earlier this year. The firm has a strong focus on the hybrid transmission concept, which it says promises a step forward on the path to electrification, with a compact and elegant package and full hybrid capabilities.
The company’s EMR3 unit meanwhile is a single speed transmission for battery electric vehicles, designed for a maximum input torque of 270Nm and max input speed of 14000rpm. The lubrication concept has been developed to offer versatility in term of installation angle to allow compatibility with different vehicle layouts.
Alternative fuels development and research are of importance for