Hydraulic excavators move with a lot of power generated by a large engine and, like a truck, this will overheat if not properly cooled. To keep things running smoothly, several cooling components are built into the design, such as the radiator, oil cooler and intercooler, which all need wind to function properly.
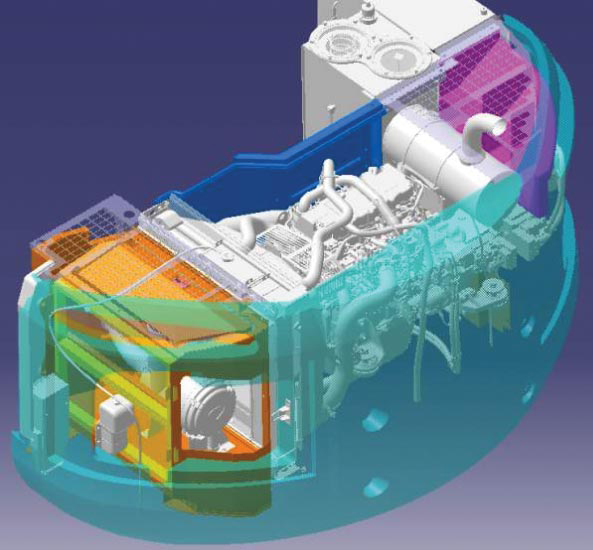
To create a wind pathway, the company started with an enclosed duct connecting the air intake port to the exhaust port, and laid out all the cooling components and the engine inside it
Hydraulic excavators move with a lot of power generated by a large engine and, like a truck, this will overheat if not properly cooled. To keep things running smoothly, several cooling components are built into the design, such as the radiator, oil cooler and intercooler, which all need wind to function properly.
Unlike a truck, which sucks in air as it travels, the excavator stays mainly in one place while working, requiring a fast-spinning fan to provide the cooling components with the wind they need.
The fan and the cooling components are seen as parts of one overall cooling system, and now5895 New Holland Kobelco has introduced "the next step" in cooling system evolution: its exclusive iNDr (integrated noise and dust reduction cooling system), which it says is a "world first."
Several things can be done to improve a cooling system's effectiveness, but excavators need more than just cooling efficiency, and in today's market there is high demand for compact designs that cannot accommodate large cooling components, says New Holland Kobelco.
"Large cooling fans are noisy, and large intake ports not only leak even more operating noise into the surroundings but also allow dust to penetrate, making cleaning difficult. Hydraulic excavators are evolving in the direction of smaller swing radii, lower noise, and easier maintenance, and these goals all conflict with the need for greater cooling efficiency. In the past, the ideals of quiet operation and easy maintenance have often been sacrificed in order to keep the engine cool."
According to the company, in contrast to conventional systems, which use a large fan near the intake port to cool the engine, iNDr creates a 'wind pathway' that naturally introduces air into the system with a fan located further inside the machine. Air transmits heat, carries dust, and vibrates with sound.
"Control the air, and all other problems can be solved. "This is what the wind pathway approach makes possible. To create a wind pathway, we started with an enclosed duct that connects the air intake port to the exhaust port, and laid out all of the cooling components and the engine inside it. This is the basic iNDr concept. Because the air can only enter and exit at certain, concentrated points, it becomes much easier to reduce noise and prevent dust penetration."
Acoustic engineers at New Holland Kobelco started in 2001 to work on the Ultimate Low-Noise Project (a 10dB reduction in operating noise), "a tremendous challenge that some said was impossible."
Different noise standards apply to hydraulic excavators, depending on engine, but because iNDr allowed New Holland Kobelco to build excavators that are much quieter than regulatory requirements, it needed a new term to show that conventional noise categories do not apply: Ultimate Low-Noise.
New Holland Kobelco models equipped with iNDr include the E70BSR, E80BMSR, E135BSR, E150B Blade Runner (all 95dB declared, 93dB measured value), and E225BSR and E235BSR (both 97dB declared, 95dB measured value).
This is compiled from a fuller report containing more technical information and details of the development of iNDr, which can be found at %$Linker:External 0 0 0 oLinkExternal www.worldhighways.com world highways false http://www.worldhighways.com/ false false %>
Unlike a truck, which sucks in air as it travels, the excavator stays mainly in one place while working, requiring a fast-spinning fan to provide the cooling components with the wind they need.
The fan and the cooling components are seen as parts of one overall cooling system, and now
Several things can be done to improve a cooling system's effectiveness, but excavators need more than just cooling efficiency, and in today's market there is high demand for compact designs that cannot accommodate large cooling components, says New Holland Kobelco.
"Large cooling fans are noisy, and large intake ports not only leak even more operating noise into the surroundings but also allow dust to penetrate, making cleaning difficult. Hydraulic excavators are evolving in the direction of smaller swing radii, lower noise, and easier maintenance, and these goals all conflict with the need for greater cooling efficiency. In the past, the ideals of quiet operation and easy maintenance have often been sacrificed in order to keep the engine cool."
According to the company, in contrast to conventional systems, which use a large fan near the intake port to cool the engine, iNDr creates a 'wind pathway' that naturally introduces air into the system with a fan located further inside the machine. Air transmits heat, carries dust, and vibrates with sound.
"Control the air, and all other problems can be solved. "This is what the wind pathway approach makes possible. To create a wind pathway, we started with an enclosed duct that connects the air intake port to the exhaust port, and laid out all of the cooling components and the engine inside it. This is the basic iNDr concept. Because the air can only enter and exit at certain, concentrated points, it becomes much easier to reduce noise and prevent dust penetration."
Acoustic engineers at New Holland Kobelco started in 2001 to work on the Ultimate Low-Noise Project (a 10dB reduction in operating noise), "a tremendous challenge that some said was impossible."
Different noise standards apply to hydraulic excavators, depending on engine, but because iNDr allowed New Holland Kobelco to build excavators that are much quieter than regulatory requirements, it needed a new term to show that conventional noise categories do not apply: Ultimate Low-Noise.
New Holland Kobelco models equipped with iNDr include the E70BSR, E80BMSR, E135BSR, E150B Blade Runner (all 95dB declared, 93dB measured value), and E225BSR and E235BSR (both 97dB declared, 95dB measured value).
This is compiled from a fuller report containing more technical information and details of the development of iNDr, which can be found at %$Linker:












