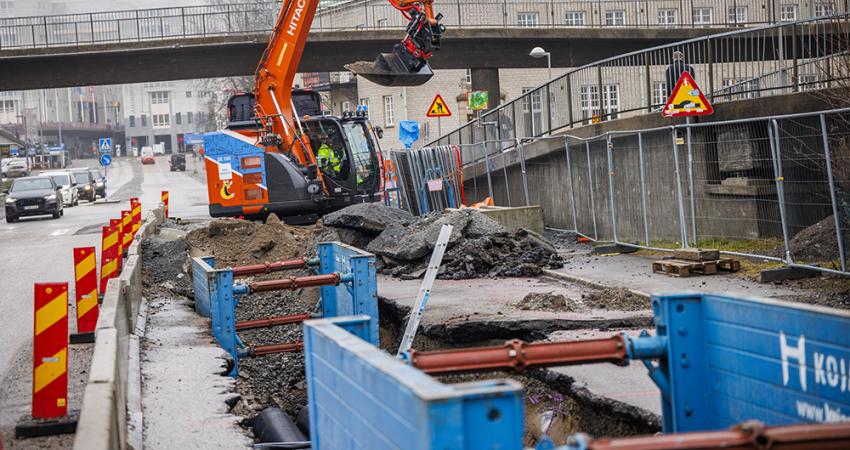
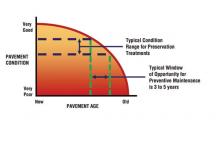
Ever since the first wheel travelled along its first path, roads have needed regular maintenance in order to provide the safest route possible to one's desired destination. For today's roads, the maintenance activities that must be performed, their scheduling and the methods of execution are in a continuing state of evolution. And this requires a significant amount of planning by those who operate and manage the road systems.

Brian T. Harris, Chairman of IRF Washington and President of Vidrifa Consulting.
Ever since the first wheel travelled along its first path, roads have needed regular maintenance in order to provide the safest route possible to one's desired destination. For today's roads, the maintenance activities that must be performed, their scheduling and the methods of execution are in a continuing state of evolution. And this requires a significant amount of planning by those who operate and manage the road systems.
In these tight financial times, government agencies are faced with uncertain fiscal conditions and tax dollars are being siphoned for many new programmes. As a result, governments must seek ways to stretch their allocations by looking at non-conventional methods to accomplish their maintenance.
Outsourcing part or all of the maintenance efforts through Public-Private Partnerships provides one solution to improving quality while maintaining or reducing costs. Some feedback from a recent survey of state and local government agencies has identified a number of reasons for going to contract maintenance.
These reasons include:
Maintenance contracting has been used in a variety of locations around the world long enough to draw some basic conclusions about its effectiveness. Given sufficient time to plan, organise and execute a well thought out programme, maintenance contracting can deliver the required services to provide a safe travel environment and prolong the life of a facility.
The ability of highway agencies to enter into maintenance by contract agreements gives policy makers and administrators a new solution for maintaining and rehabilitating their roadways. If properly structured, the arrangement shifts the burden of operations and expense to the private sector while ensuring that the assets are adequately maintained.
As part of the2462 IRF commitment to provide technology transfer and training to the highway community worldwide, IRF will be holding its 14th Annual Seminar on Contract Maintenance & Asset Management from 25 October to 3 November, 2009. Please join us in Orlando, Florida, to learn new strategies for funding a contract maintenance programme, as well as lessons learned from programmes already underway throughout the world from experts from around the world.
In these tight financial times, government agencies are faced with uncertain fiscal conditions and tax dollars are being siphoned for many new programmes. As a result, governments must seek ways to stretch their allocations by looking at non-conventional methods to accomplish their maintenance.
Outsourcing part or all of the maintenance efforts through Public-Private Partnerships provides one solution to improving quality while maintaining or reducing costs. Some feedback from a recent survey of state and local government agencies has identified a number of reasons for going to contract maintenance.
These reasons include:
- reducing costs
- increasing efficiency
- improving quality
- reducing time delays
- reducing risk
- reducing personnel and training requirements, and
- enhancing innovation.
Maintenance contracting has been used in a variety of locations around the world long enough to draw some basic conclusions about its effectiveness. Given sufficient time to plan, organise and execute a well thought out programme, maintenance contracting can deliver the required services to provide a safe travel environment and prolong the life of a facility.
The ability of highway agencies to enter into maintenance by contract agreements gives policy makers and administrators a new solution for maintaining and rehabilitating their roadways. If properly structured, the arrangement shifts the burden of operations and expense to the private sector while ensuring that the assets are adequately maintained.
As part of the